1
/
of
10
MELATONIN
- Regular price
-
₹530.00 - Regular price
-
- Sale price
-
₹530.00
Tax included.
Shipping calculated at checkout.

Couldn't load pickup availability
Additional Information
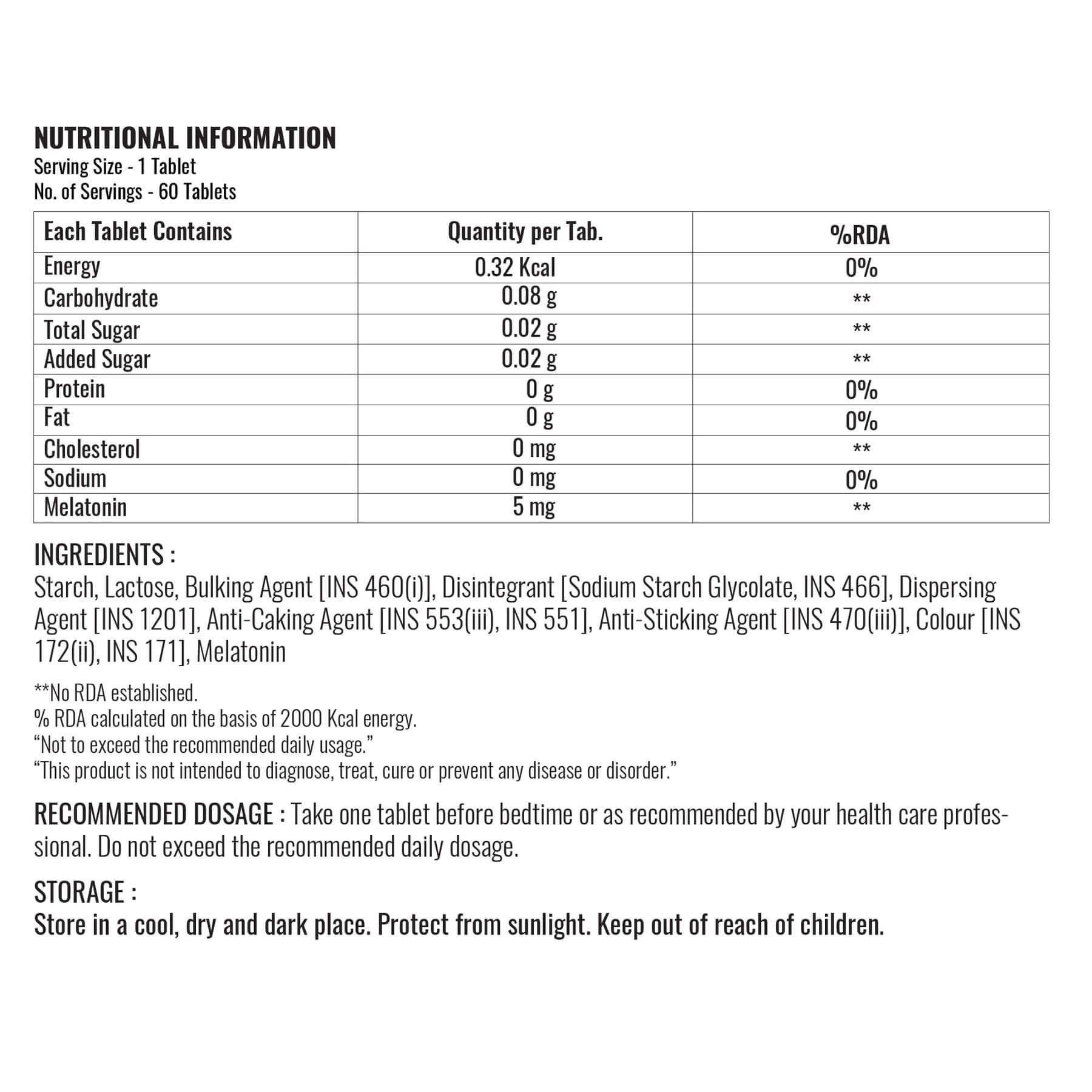
| Name and Address of the Manufacturer: | Supermax Drugs & Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd., Khasra No.322, Nanhera, Anantpur, Bhagwanpur, Roorkee, Haridwar(Uttarakhand)-247668, India |
| Name and Address of the Packer: | Supermax Drugs & Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd., Khasra No.322, Nanhera, Anantpur, Bhagwanpur, Roorkee, Haridwar(Uttarakhand)-247668, India |
| Common or Generic Name: | Melatonin |
| Country of Origin: | India |
| Item Net Weight: | 42 g |
| Item Dimensions (LxWxH): | Pack of 60 Tablets: 7X7.6X13 Centimeters |
| Net Quantity: | 60 Tablets |
| Flavour Name: | N/A |
| Pack Options and Prices: | 60 Tablets Bottle MRP: Rs 530.00 (Inclusive of all taxes) Single Tablet cost: Rs 8.83 |
| Consumer Care Details: | Address: C-14, Sector 85, Noida - 201 305, U.P. INDIA Telephone number: +91 7428007230 E-mail address: info@steadfastnutrition.in |










MELATONIN
- Regular price
-
₹530.00 - Regular price
-
- Sale price
-
₹530.00












